概括来说:UnLua 绑定了 UE 创建对象的事件,当创建 CDO 时会调用到 UnLua 的 NotifyUObjectCreated,在其中拿到了该对象的 UClass,对该对象的 UClass 中的 UFUNCTION 通过SetNativeFunc 修改为 CallLua 函数,这样就实现了覆写 UFUNCTION。
下面来具体分析一下实现。UnLua 实现覆写完整的调用栈:
替换 Thunk 函数 在 UnLua 的 FLuaContext 的 initialize 函数中,将 GLuaCxt 注册到了 GUObjectArray 中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 if (!bAddUObjectNotify){ GUObjectArray.AddUObjectCreateListener (GLuaCxt); GUObjectArray.AddUObjectDeleteListener (GLuaCxt); }
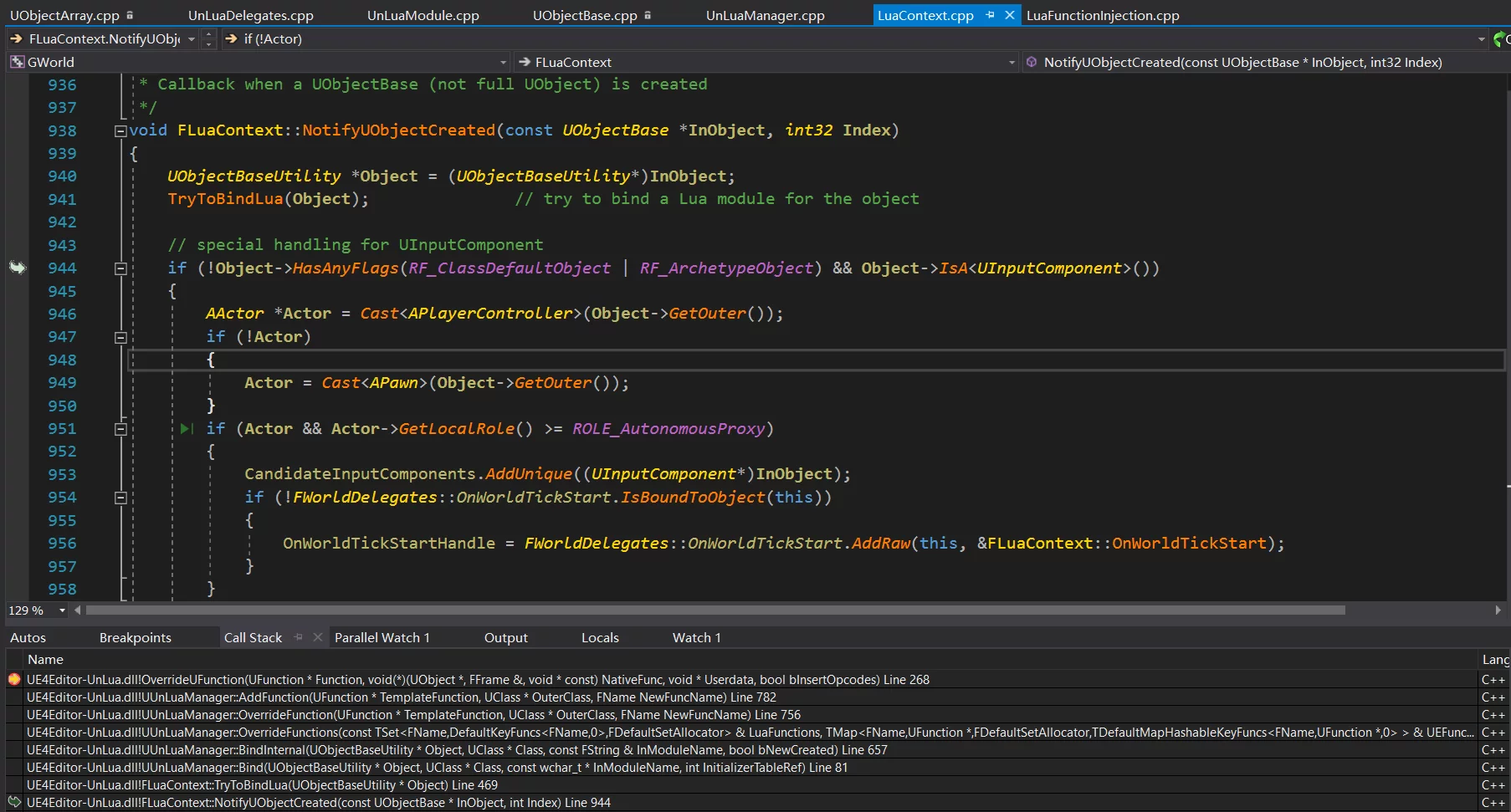
而 FLuaContext 继承自 FUObjectArray::FUObjectCreateListener 和FUObjectArray::FUObjectDeleteListener,所以当 UE 的对象系统创建对象的时候会把调用到 FLuaContext 的 NotifyUObjectCreated 与NotifyUObjectDeleted。
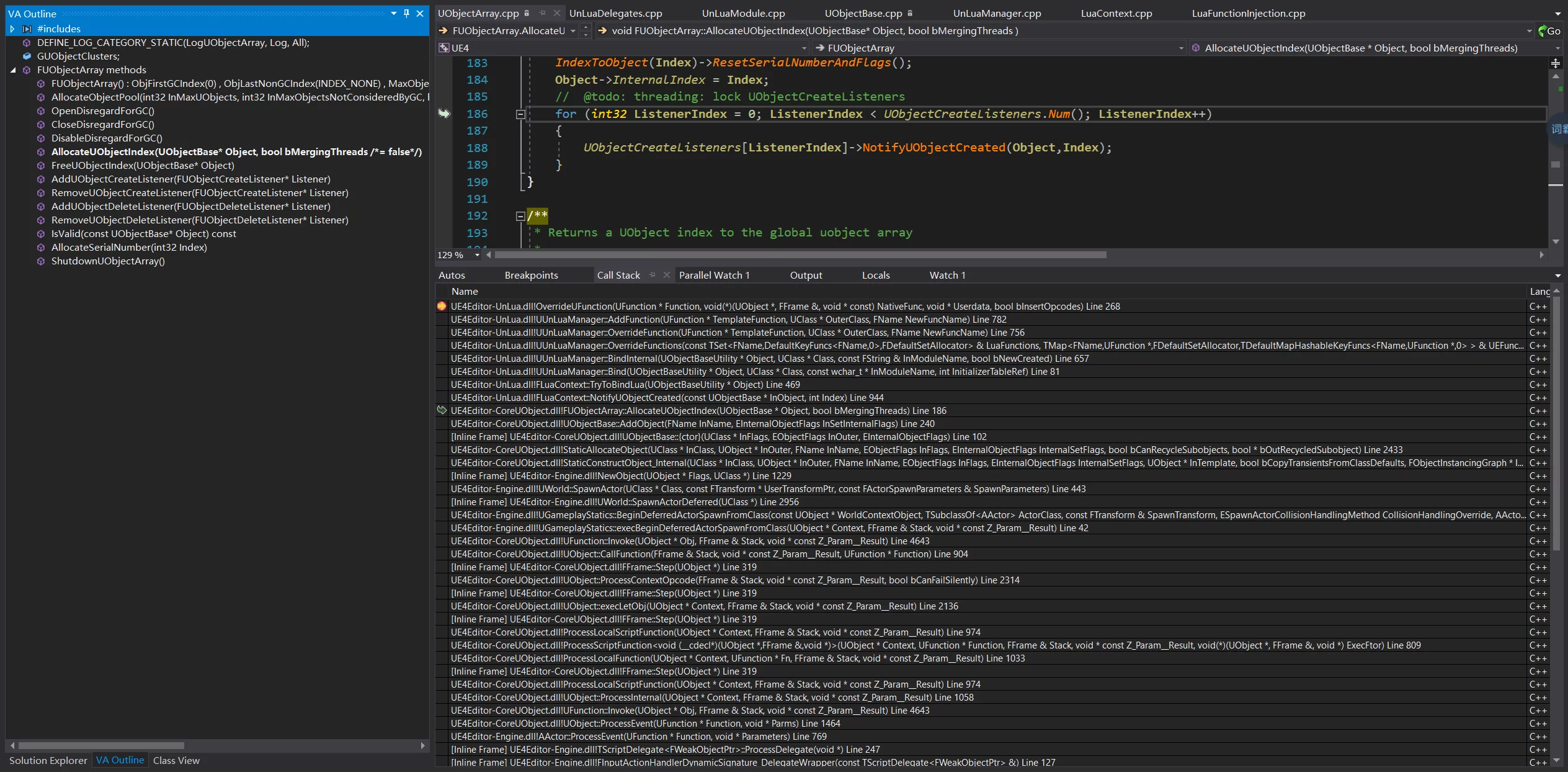
当创建一个 UObject 的时候会在 FObjectArray 的AllocateUObjectIndex中对多有注册过的 CreateListener 调用 NotifyUObjectDeleted 函数。
而 UnLua 实现覆写 UFUNCTION 的逻辑就是写在 NotifyUObjectCreated 中的 TryBindLua 调用中,栈如下:
FLuaContext::TryBindUnlua 1 2 bool FLuaContext::TryToBindLua (UObjectBaseUtility *Object)
主要作用是:如果创建的对象继承了 UUnLuaInterface,具有GetModuleName 函数,则通过传进来的 UObject 获取到它的 UCclass,然后再通过 UClass 得到 GetModuleName 函数的UFunction,并通过 CDO 对象调用该 UFunction,得到该 CLass 绑定的 Lua 模块名。
若没有静态绑定,则检查是否具有动态绑定。
UUnLuaManager::Bind 该函数定义在 UnLua/pRIVATE/UnLuaManager.cpp 文件中。
在 TryBindUnlua 中得到了当前创建对象的 UClass 和绑定的模块名,传递到了 Bind 函数中,它主要做了几件事情:
注册 Class 到 lua
require 对应的 lua 模块
调用 UnLuaManager::BindInternal 函数
为当前对象创建一个 lua 端对象并 push 上一个 Initialize 函数并调用
BindInternal 其中的关键函数为UnLuaManager::BindInternal:
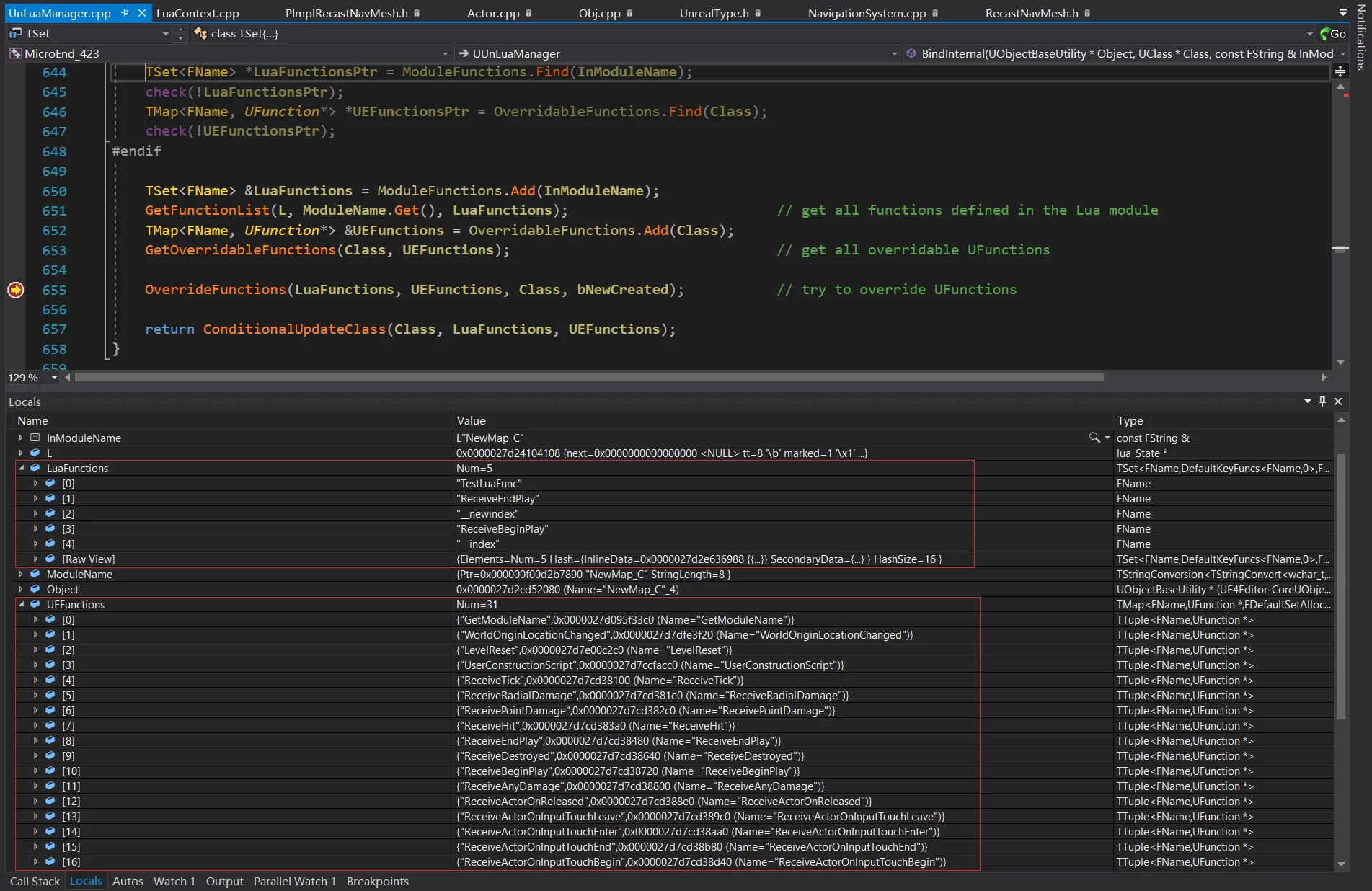
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 bool UUnLuaManager::BindInternal (UObjectBaseUtility *Object, UClass *Class, const FString &InModuleName, bool bNewCreated) if (!Object || !Class) { return false ; } lua_State *L = *GLuaCxt; TStringConversion<TStringConvert<TCHAR, ANSICHAR>> ModuleName (*InModuleName); if (!bNewCreated) { if (!BindSurvivalObject (L, Object, Class, ModuleName.Get ())) { return false ; } FString *ModuleNamePtr = ModuleNames.Find (Class); if (ModuleNamePtr) { return true ; } } ModuleNames.Add (Class, InModuleName); Classes.Add (InModuleName, Class); #if UE_BUILD_DEBUG TSet<FName> *LuaFunctionsPtr = ModuleFunctions.Find (InModuleName); check (!LuaFunctionsPtr); TMap<FName, UFunction*> *UEFunctionsPtr = OverridableFunctions.Find (Class); check (!UEFunctionsPtr); #endif TSet<FName> &LuaFunctions = ModuleFunctions.Add (InModuleName); GetFunctionList (L, ModuleName.Get (), LuaFunctions); TMap<FName, UFunction*> &UEFunctions = OverridableFunctions.Add (Class); GetOverridableFunctions (Class, UEFunctions); OverrideFunctions (LuaFunctions, UEFunctions, Class, bNewCreated); return ConditionalUpdateClass (Class, LuaFunctions, UEFunctions); }
这个函数接受到的参数是创建出来的 UObject,以及它的 UClass,还有对应的 Lua 的模块名。
把对象的 UClass 与 Lua 的模块名对应添加到 ModuleNames 和Classes中
从 Lua 端通过 L 获取所指定模块名中的所有函数
从 UClass 获取所有的 BlueprintEvent、RepNotifyFunc 函数
对两边获取的结果调用 UUnLuaManager::OverrideFunctions 执行替换
UUnLuaManager::OverrideFunctions 对从 Lua 端获取的函数使用名字在当前类的 UFunction 中查找,依次对其调用UUnLuaManager::OverrideFunction.
UUnLuaManager::OverrideFunction
判断传入的 UFunction 是不是属于传入的 Outer UClasss
判断是否允许调用被覆写的函数
调用 AddFunction 函数
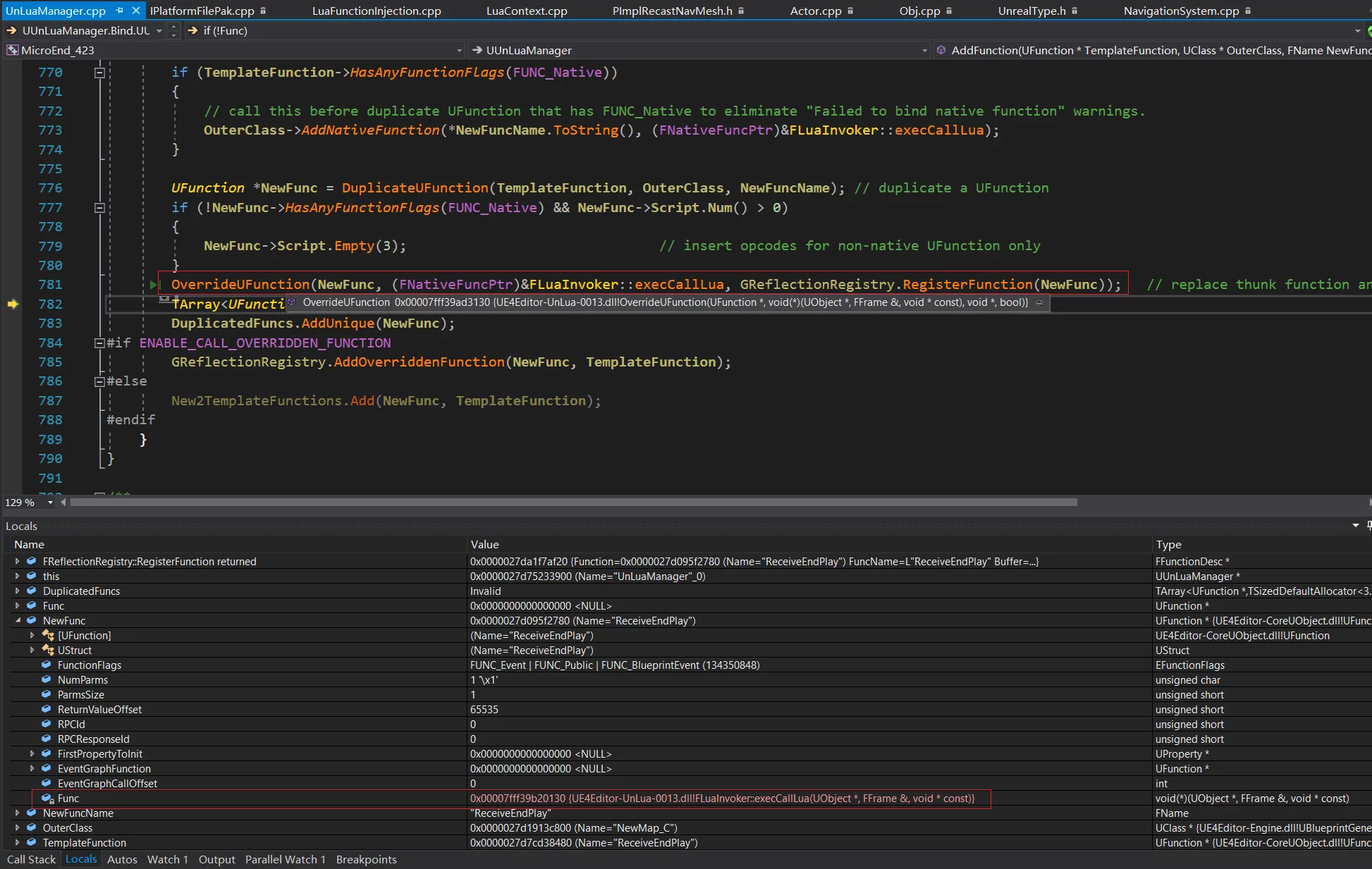
UUnLuaManager::AddFunction
如果函数为 FUNC_Native 则将 FLuaInvoker::execCallLua 和所覆写的函数名通过 AddNativeFunction 添加至 UClass
将 UFunction 内的函数指针替换为(FNativeFuncPtr)&FLuaInvoker::execCallLua
如果开启了允许调用被覆写的函数,则把替换 NativeFunc 之前的 UFunction 对象存到 GReflectionRegistry 中
Call lua 首先,需要说的一点是,当使用 UEC++ 写的带有 UFUNCTION 并具有 BlueprintNativeEvent 或者 BlueprintImplementableEvent 标记的函数,UHT 会给生成对应名字的函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 UFUNCTION (BlueprintNativeEvent,BlueprintCallable) bool TESTFUNC () bool TESTFUNC_Implementation () UFUNCTION (BlueprintImplementableEvent, meta = (DisplayName = "BeginPlay" )) bool TESTImplEvent (AActor* InActor,int32 InIval)
UHT 生成的函数和传递的数据结构:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #define MicroEnd_423_Source_MicroEnd_423_Public_MyActor_h_13_EVENT_PARMS \ struct MyActor_eventReceiveBytes_Parms \ { \ TArray<uint8> InData; \ }; \ struct MyActor_eventTESTFUNC_Parms \ { \ bool ReturnValue; \ \ \ MyActor_eventTESTFUNC_Parms() \ : ReturnValue(false) \ { \ } \ }; \ struct MyActor_eventTESTImplEvent_Parms \ { \ AActor* InActor; \ int32 InIval; \ bool ReturnValue; \ \ \ MyActor_eventTESTImplEvent_Parms() \ : ReturnValue(false) \ { \ } \ }; static FName NAME_AMyActor_TESTFUNC = FName (TEXT ("TESTFUNC" ));bool AMyActor::TESTFUNC () MyActor_eventTESTFUNC_Parms Parms; ProcessEvent (FindFunctionChecked (NAME_AMyActor_TESTFUNC),&Parms); return !!Parms.ReturnValue; } static FName NAME_AMyActor_TESTImplEvent = FName (TEXT ("TESTImplEvent" ));bool AMyActor::TESTImplEvent (AActor* InActor, int32 InIval) MyActor_eventTESTImplEvent_Parms Parms; Parms.InActor=InActor; Parms.InIval=InIval; ProcessEvent (FindFunctionChecked (NAME_AMyActor_TESTImplEvent),&Parms); return !!Parms.ReturnValue; }
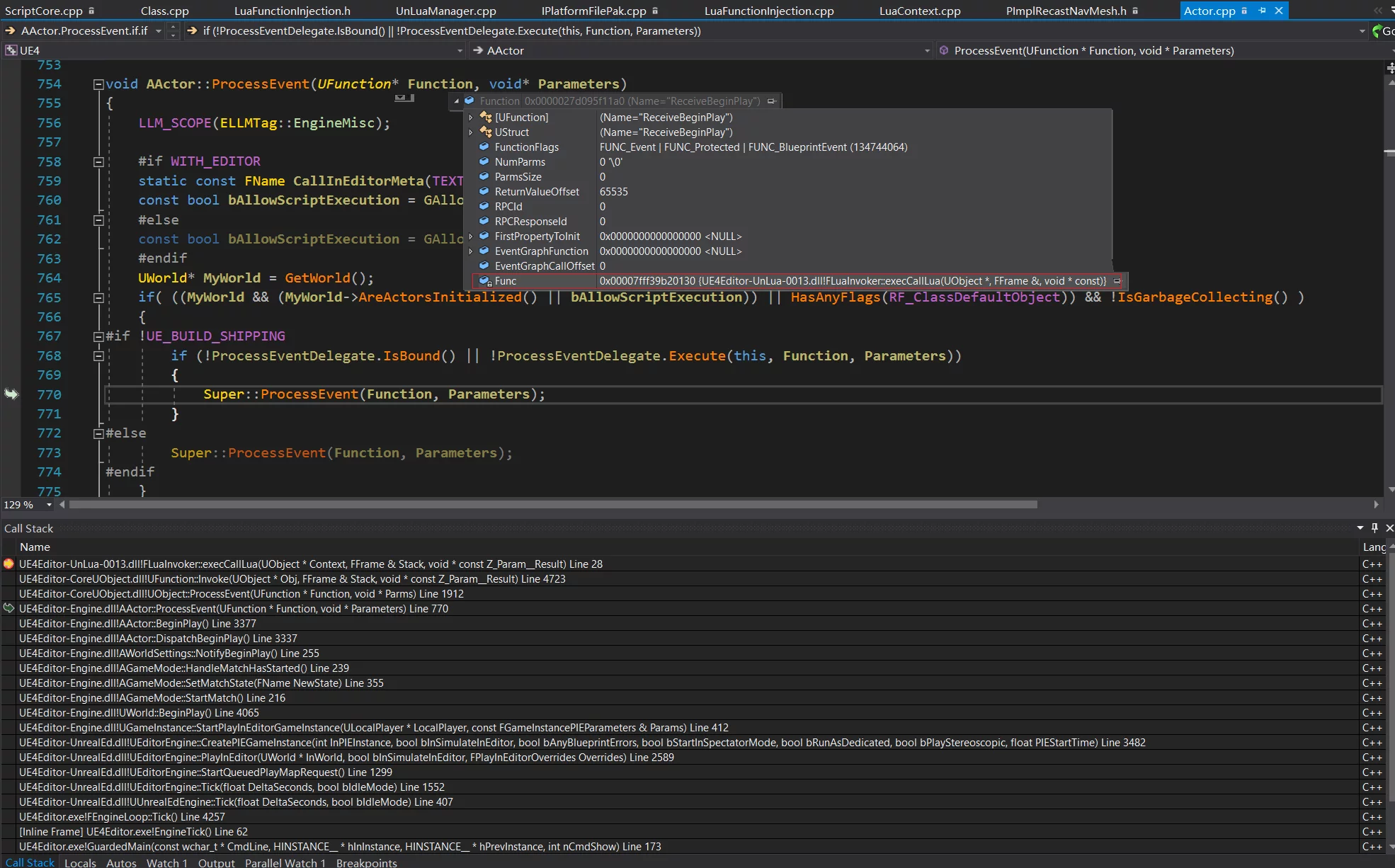
可以看到,UHT 帮我们定义了同名函数,并将其转发给ProcessEvent。
注意:这里通过 FindFunctionChecked 方法是调用的UObject::FindFunctionChecked:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 UFunction* UObject::FindFunction (FName InName) const return GetClass ()->FindFunctionByName (InName); } UFunction* UObject::FindFunctionChecked (FName InName) const UFunction* Result = FindFunction (InName); if (Result == NULL ) { UE_LOG (LogScriptCore, Fatal, TEXT ("Failed to find function %s in %s" ), *InName.ToString (), *GetFullName ()); } return Result; }
可以看到,这里传递给 ProcessEvent 的UFunction*就是从当前对象的 UClass 中得到的。
经过前面分分析可以知道,UnLua 实现的函数覆写,就是把 UClass 中的 UFunction 中的原生 thunk 函数指针替换为 FLuaInvoker::execCallLua,而且当一个对象的BlueprintNativeEvent 和BlueprintImplementableEvent函数被调用的时候会调用到 ProcessEvent 并传入对应的 UFunction*,在ProcessEvent 中又调Invork(调用其中的原生指针),也就是实现调用到了 unlua 中替换绑定的FLuaInvoker::execCallLua,在这个函数中再转发给调用 lua 端的函数,从而实现了覆写函数的目的。